How Diet Influences Flexibility: Fueling Your Body for Movement
Flexibility is often associated with stretching and physical exercises, but did you know that what you eat plays a significant role in how flexible your body can be? The nutrients you consume can impact your muscle elasticity, joint health, and overall mobility, making diet an essential component of any flexibility-focused fitness routine.
The Connection Between Diet and Flexibility
When you think of flexibility, your mind might immediately go to yoga poses or stretching routines. However, flexibility is more than just muscle pliability—it’s also about the health of your connective tissues, such as tendons and ligaments, and the mobility of your joints. Certain nutrients and foods can enhance these aspects of flexibility, while others can hinder them.
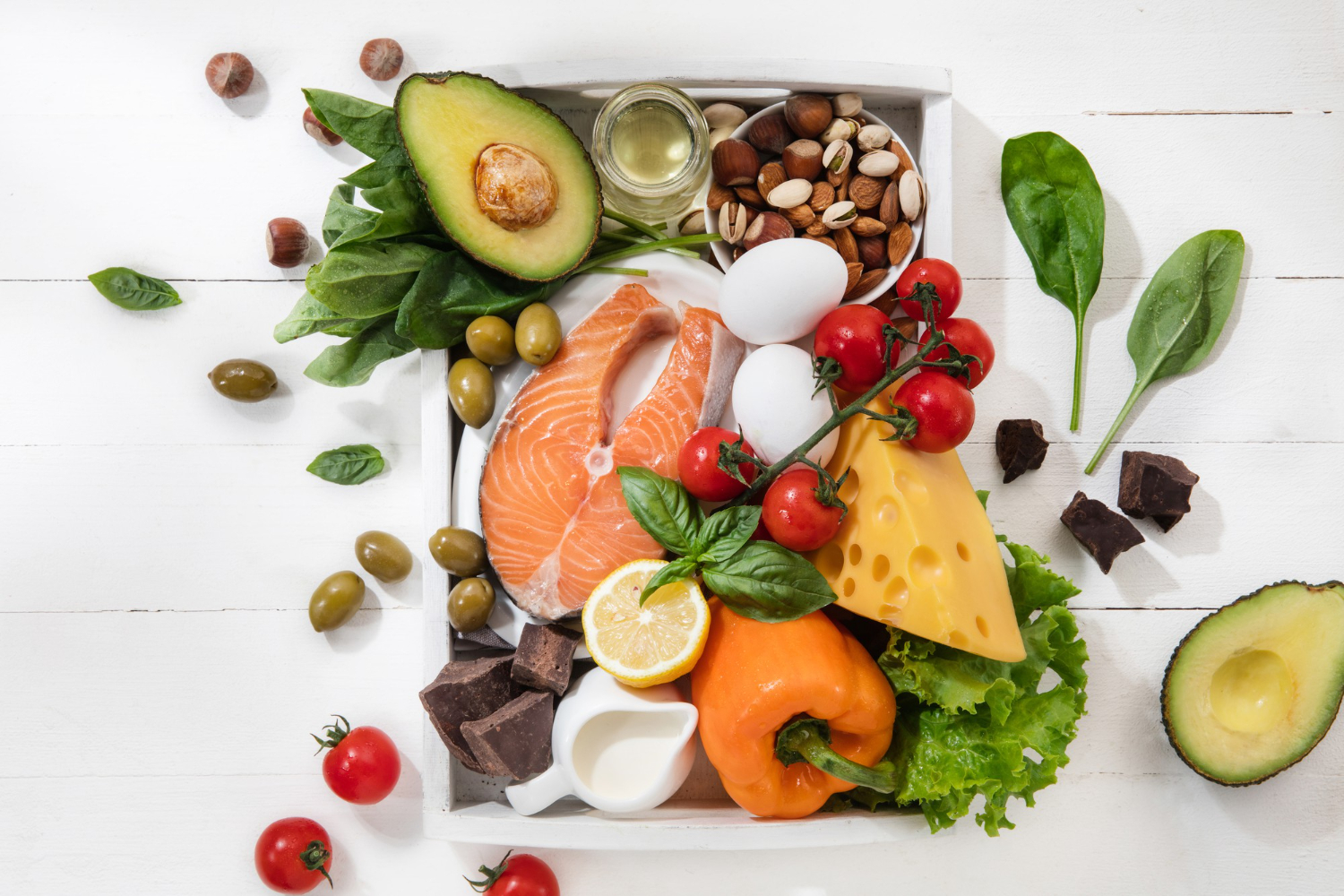
Key Nutrients That Improve Flexibility
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Found in fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts, omega-3s help reduce inflammation in the body, promoting joint health and flexibility.
- Collagen: Consuming collagen-rich foods like bone broth or taking collagen supplements can support healthy joints and connective tissues.
- Vitamin C: This vitamin is crucial for collagen production and helps maintain the strength of tendons and ligaments.
- Magnesium: Found in leafy greens, nuts, and seeds, magnesium helps relax muscles, reducing stiffness and improving flexibility.
- Hydration: Staying hydrated keeps your muscles supple and prevents cramping, which is vital for flexibility.
Foods to Avoid for Better Flexibility
- Processed Sugars: Excess sugar can lead to inflammation, which may limit flexibility and cause stiffness.
- Trans Fats: Often found in fried and processed foods, trans fats contribute to inflammation and poor joint health.
- Excessive Salt: High sodium intake can lead to dehydration and muscle cramps, affecting flexibility.
Tips for a Flexibility-Boosting Diet
- Incorporate Anti-Inflammatory Foods: Include plenty of fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats in your diet.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink enough water to keep your muscles hydrated and flexible.
- Balance Your Meals: Ensure you’re getting a mix of protein, healthy fats, and complex carbohydrates to support overall muscle and joint health.
Conclusion
Flexibility isn’t just about how much you stretch—it’s also about how you nourish your body. By focusing on a diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, staying hydrated, and avoiding inflammatory triggers, you can enhance your flexibility and support your body’s range of motion. Pair a healthy diet with consistent stretching and exercise, and you’ll see improvements in your flexibility in no time!